Gitlab-CI and Auto Deployment to Remote Server
You can create auto deployments for your project when there is a commit to specific branch. Let’s say you want to deploy a java project to docker on a different host. We have these:
git.msdalp.comwhere gitlab is installedproduction.msdalp.comis the server for production deployment from master.
If the gitlab is just installed then you probably don’t have runners. Runners are used for building and deploying the code.
First install gitlab-runner from this page https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/install/linux-repository.html.
Then add docker runners to your system for building docker projects.
Since I had ubuntu server followed these to install runners:
# For Debian/Ubuntu/Mint
curl -L https://packages.gitlab.com/install/repositories/runner/gitlab-runner/script.deb.sh | sudo bash
# For Debian/Ubuntu/Mint
sudo apt-get install gitlab-runnerVisit the page https://git.msdalp.com/admin/runners and get the runner keys from lower box. You need the change the url with your gitlab domain.
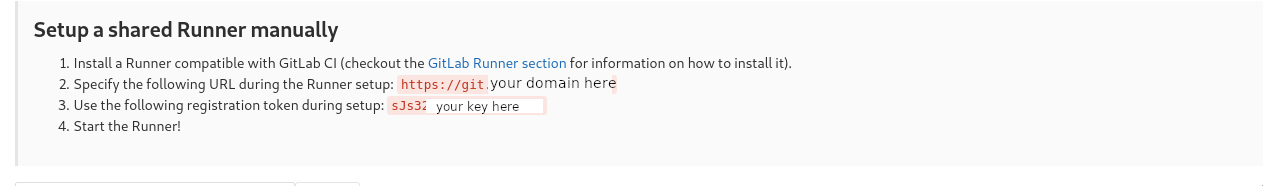
Then add docker-builder and docker-runner runners.
sudo gitlab-runner register -n --url https://git.msdalp.com --registration-token YOUR_TOKEN --executor shell --description "Docker Builder"sudo gitlab-runner register -n --url https://git.msdalp.com --registration-token YOUR_TOKEN --executor docker --description "Docker Runner" --docker-image "docker:stable" --docker-privilegedIf you go back to page https://git.msdalp.com/admin/runners you should see both runners below.
We can either deploy sending the files to remote server and use docker build on there or build on gitlab server and push to docker repository. Second option is better in general but since I don’t have google image repository permissions right now I will go with the first one.
Make sure you disabled docker-builder from shared runners. Since it is a shell executer it might work differently and if both are active it would select randomly for build process. I was asked before why the builds are randomly failing and this might be your reason as well.
Create a user on the deployment server with only docker group permissions and nothing else. On the production server:
$ sudo useradd test_app -m -d /home/deployment/test_app/
This will create the test_app user with home directory /home/deployment/test_app. Next generate ssh keys with
$ ssh-keygen
Create a deployment key on your local or on any server but be aware it will give access to production server.
Next add the created deployment public key .ssh/id_rsa.pub to production server’s authorized_keys. You can do it manually as
$ nano /home/deployment/test_app/.ssh/authorized_keys and paste the id_rsa.pub you copied from deployment key.
Also make sure you have proper permission for ssh folder:
$ chmod 700 /home/deployment/test_app/.ssh
$ chmod 400 /home/deployment/test_app/.ssh/authorized_keys
$ chown test_app:test_app /home/deployment/test_app -R
Now you should be able to ssh into production server by using deployment key as ssh test_app@production.msdalp.com.
Before adding the gitlab-ci file we need to set environment variables first. Go to the page https://git.msdalp.com/test_app/settings/ci_cd and set these two variables.
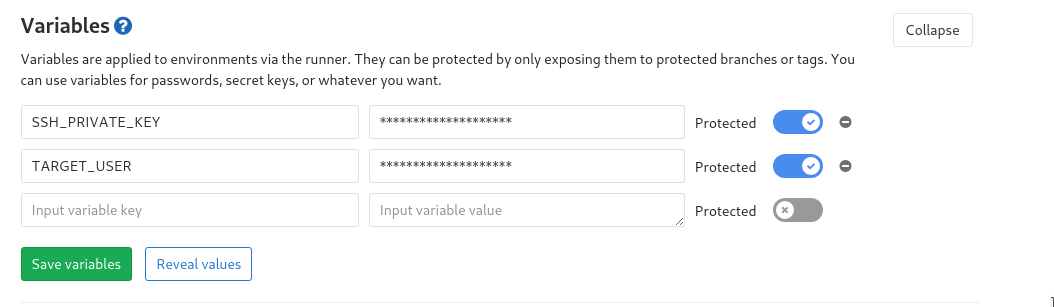
SSH_PRIVATE_KEY is the private key we created for deployment. You will copy everything from id_rsa file and put here. TARGET_USER is just the username and server address for production server which is test_app@production.msdalp.com in this case.
Next we can add .gitlab-ci.yml and ssh into our production server when there is a commit on master. The simplest file would be:
image: alpine
variables:
before_script:
- 'which ssh-agent || ( apk add openssh-client)'
##
## Run ssh-agent (inside the build environment)
##
- eval "$(ssh-agent -s)"
##
## Add the SSH key stored in SSH_PRIVATE_KEY variable to the agent store
## We're using tr to fix line endings which makes ed25519 keys work
## without extra base64 encoding.
## https://gitlab.com/gitlab-examples/ssh-private-key/issues/1#note_48526556
##
- echo "$SSH_PRIVATE_KEY" | tr -d '\r' | ssh-add - > /dev/null
##
## Create the SSH directory and give it the right permissions
##
- mkdir -p ~/.ssh
- chmod 700 ~/.ssh
- ssh-keyscan -H 'your ip or domain' >> ~/.ssh/known_hosts
build:
stage: build
script:
## we need this hostkeychecking at first since it didn't verify the target host yet. you either verify it
## manually or leave it on first command to do it. Not really sure if it is the best way of handling this.
- ssh -o "StrictHostKeyChecking=no" -p22 $TARGET_USER "mkdir -p /home/deployment/test_app/app/"
- scp -P22 -r ./* $TARGET_USER:/home/deployment/test_app/app/
- ssh -p22 $TARGET_USER "docker build -t test_app /home/deployment/test_app/app/"
- ssh -p22 $TARGET_USER "docker run -d -it test_app"